The Impact of Oxidative Stress on the Aging Process
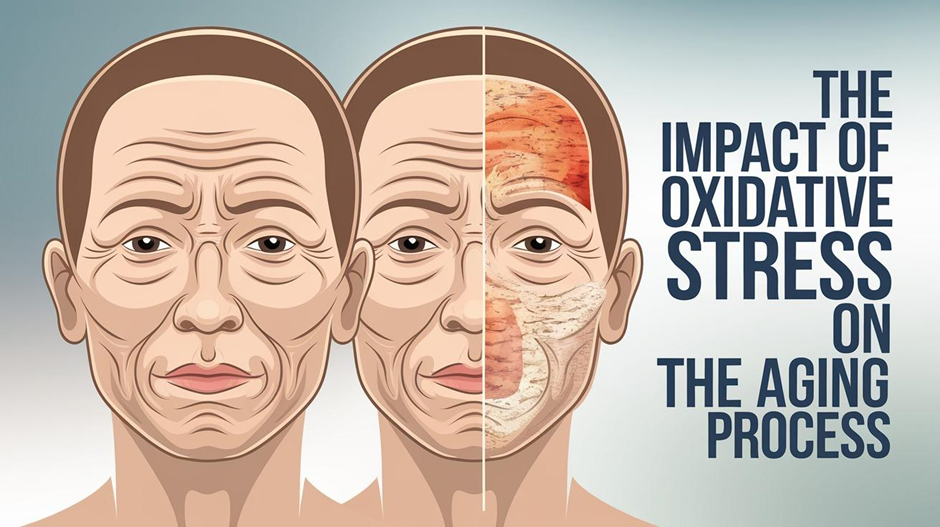
Aging is a multifactorial process influenced by genetics, environment, and metabolism, with oxidative stress playing a central role. This occurs when reactive oxygen species (ROS) surpass the body’s ability to neutralize them, resulting in cellular damage and increased vulnerability to age-related conditions. Exploring the world of NMN supplementation has revealed its potential in combating oxidative stress by enhancing cellular repair and promoting healthier aging.
The Biological Basis of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when free radicals—unstable molecules with unpaired electrons—interact with cellular components such as DNA, proteins, and lipids. These interactions cause structural damage, disrupt cellular signaling, and impair mitochondrial function. Over time, the accumulation of oxidative damage contributes to cellular senescence, chronic inflammation, and tissue degeneration, all hallmarks of aging.
Mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles within cells, are particularly susceptible to oxidative stress. As the primary source of ROS during energy metabolism, dysfunctional mitochondria exacerbate oxidative damage, creating a vicious cycle of cellular decline. Addressing oxidative stress is therefore critical for preserving mitochondrial health and promoting cellular longevity.
The Role of NMN in Combating Oxidative Stress
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) plays a vital role in counteracting oxidative stress by supporting cellular repair mechanisms and energy production. NMN is a precursor to NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a coenzyme essential for mitochondrial function, DNA repair, and the regulation of oxidative stress. By replenishing NAD+ levels, NMN enhances the cell’s ability to neutralize free radicals and repair oxidative damage.
Research shows that NMN supplementation improves mitochondrial efficiency, reducing the production of ROS and enhancing the cell’s antioxidant defenses. Furthermore, NMN activates sirtuins, a family of NAD+-dependent proteins that regulate inflammation, stress responses, and metabolic health. These effects collectively mitigate the impact of oxidative stress on cellular aging and enhance resilience against age-related diseases.
Towards a New Understanding of Oxidative Stress and Longevity
The connection between oxidative stress and aging highlights the importance of maintaining cellular health through targeted interventions. NMN and other NAD+ precursors offer a promising approach to addressing the root causes of oxidative damage, supporting mitochondrial function, and promoting overall vitality. By integrating molecular therapies like NMN supplementation with lifestyle practices such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, it is possible to create a comprehensive strategy for extending healthspan.
As scientific exploration of oxidative stress continues, the potential to unlock new pathways for promoting cellular longevity and reducing the burden of aging-related diseases becomes increasingly tangible. By addressing oxidative damage at its source, we pave the way for a future where aging is not just managed but actively optimized, ensuring better quality of life across the lifespan.