Understanding Astigmatism and Its Solutions
Astigmatism is a common but often misunderstood vision problem that can impact daily tasks like reading or driving. This guide explains its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, including glasses and advanced correction technologies, offering clarity for those seeking solutions.
What is Astigmatism?
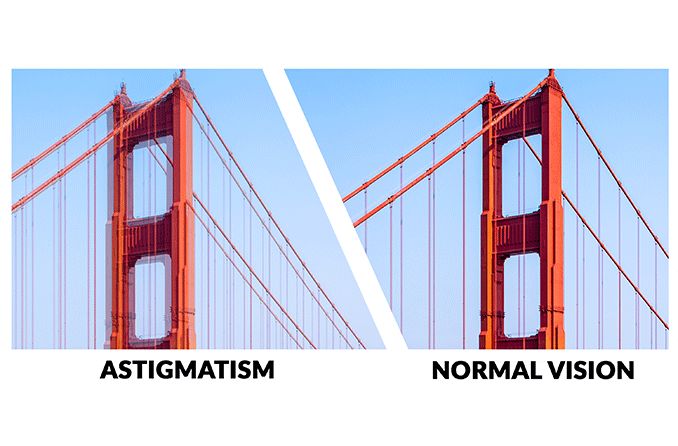
Astigmatism is a common vision condition caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, preventing light from focusing properly on the retina. Instead of light rays converging to a single point, the irregularities cause the light to scatter, leading to blurred or distorted vision.
While mild astigmatism might go unnoticed, higher degrees can create significant challenges, such as difficulty recognizing details at any distance or increased eye strain.
What Causes Astigmatism and What Are Its Symptoms?
Causes of Astigmatism
Astigmatism’s root cause is often linked to the eye’s shape. Here are some key contributing factors:
- Genetics: Astigmatism is frequently hereditary and can run in families.
- Eye Development: Certain cases appear at birth or develop during childhood as the eye grows.
- Eye Injury or Surgery: Trauma or surgical procedures can alter the cornea or lens, triggering astigmatism.
- Corneal Conditions: Disorders like keratoconus can result in irregular corneal shapes that cause or exacerbate astigmatism.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms vary, but they often include:
- Blurred or distorted vision at all distances
- Frequent headaches
- Eye strain, especially during prolonged reading or screen use
- Difficulty with night vision
- Squinting to see clearly
Any of these symptoms could indicate astigmatism or another eyesight issue, which makes regular eye check-ups essential.
How is Astigmatism Diagnosed?
Early diagnosis is crucial to managing astigmatism effectively. Comprehensive eye exams, typically performed by an optometrist or ophthalmologist, can determine the severity of the condition. A standard diagnostic process often includes:
- Visual Acuity Test: Measures how well you see small details using an eye chart.
- Keratometry/Topography: Assesses the curvature of your cornea to detect irregularities.
- Refraction Test: Identifies the lens or prescription strength needed to correct your vision.
If you suspect you have astigmatism, schedule an eye exam to confirm the diagnosis and create a tailored correction plan.
Types of Astigmatism
Not all astigmatisms are the same. Understanding their classifications helps guide treatment decisions.
Regular vs. Irregular Astigmatism
- Regular Astigmatism occurs when the cornea is evenly curved but lacks a spherical shape. It’s the most common type and is relatively easy to correct with glasses or contacts.
- Irregular Astigmatism results from uneven or asymmetrical slopes in the cornea due to injury or disease. Specialized correction methods like custom contact lenses or surgery are often required.
Corneal vs. Lenticular Astigmatism
- Corneal Astigmatism originates from an irregularly shaped cornea and is the most common.
- Lenticular Astigmatism occurs due to imperfections in the shape of the eye’s lens. Although less common, it can still disrupt vision.
Options for Correcting Astigmatism
You don’t have to live with the discomfort of unmanaged astigmatism. Several effective correction options are available:
1. Eyeglasses
Eyeglasses offer a straightforward and non-invasive way to correct astigmatism. Specially designed cylindrical lenses help focus light on the retina, restoring clear vision.
2. Contact Lenses
Contact lenses, especially toric lenses, are highly effective at correcting astigmatism. Toric lenses are uniquely crafted to address the differences in curvature that cause vision distortion.
For those with irregular astigmatism, rigid gas permeable (RGP) or hybrid contact lenses provide tailored solutions.
3. Refractive Surgery
For a more permanent solution, refractive surgeries like LASIK or PRK reshape the cornea to correct astigmatism. These procedures are quick and boast high success rates but may not be suitable for all cases—consult with your eye doctor to determine eligibility.
Innovations in Treating Astigmatism
The field of vision correction is advancing rapidly, making treatment more effective than ever.
Toric Contact Lenses
These lenses are specifically designed for astigmatism and are now available in a wide range of materials and wear schedules, ensuring comfort and convenience.
Laser Eye Surgery
Refinements in laser procedures, like LASIK surgery like those in Utah and SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction), offer precise corrections with quicker recoveries compared to traditional methods.
Custom Wavefront Technology
Wavefront-guided LASIK goes beyond standard vision correction by addressing unique irregularities in the eye, offering sharper, higher-quality vision for those with astigmatism.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Astigmatism
Managing astigmatism goes beyond correction methods. A few simple lifestyle habits can help protect your eye health and reduce symptoms:
- Follow the 20-20-20 Rule: Look 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes of screen use to reduce eye strain.
- Prioritize Lighting: Ensure proper illumination while reading or working to avoid unnecessary eye strain.
- Stay Hydrated: Dry eyes can worsen symptoms, so drink ample water and consider lubricating eye drops if needed.
- Maintain Regular Eye Exams: Early detection and updated prescriptions are critical to managing astigmatism effectively.
- Consider Eye Exercises: Certain exercises may strengthen eye muscles and improve focus, although they’re best seen as complementary rather than primary treatments.
Conclusion
Now that you know what causes astigmatism, its symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment options, be proactive about protecting your vision. Regular eye exams are vital for maintaining healthy eyes and detecting any issues early on.